Overview
SQL+ is an AddIn for Microsoft Excel. It enables the use of SQL in Excel.
Supported data sources include the local workbook, external XLS workbooks, and CSV files.
Additional features include:
- Special functions (COR,COV, REG) extending the SQL command base
- Pre-defined, parameterizable SQL patterns supporting key use cases
- Ability to name, store, and retrieve own SQL statements and to embed them in other queries, just like a view.
Basic Controls
When you open Excel and open or create a workbook, you should see the “SQL+” ribbon in the menu bar. Click on it to use the functions of SQL+.
Ribbon
- Button to open the SQL Editor, the core functionality of the AddIn.
- Convenience feature of the AddIn to define the general format of the generated results.
- Convenience features of the AddIn to define the format of text, numbers and dates of the generated results.

SQL Editor
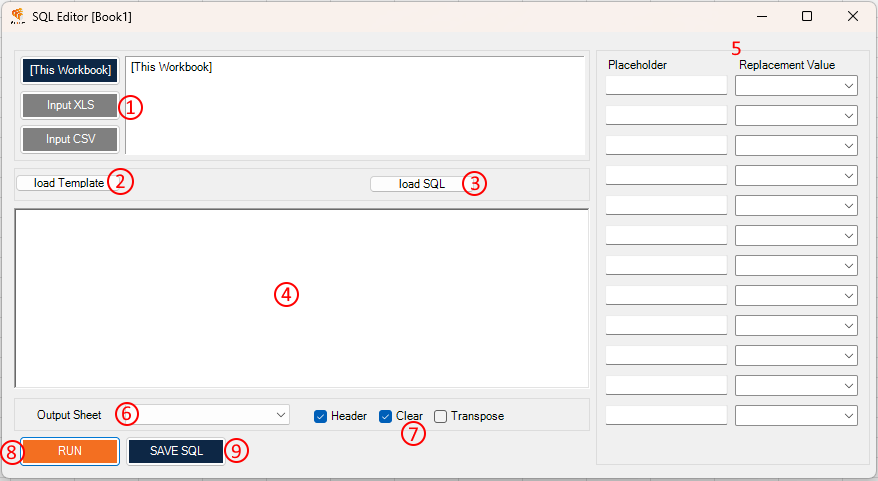
- SQL+ supports three types of data sources: the local workbook, other XLS workbooks, and CSV files. The button for the selected source is shown in blue, the buttons for the other sources are grey. By default, the local workbook (“This Workbook”) is selected. To select another source, click the respective button. For additional details on selecting and using different data sources, see the next chapter.
- Here you can select a template from the selection menu.
- Here you can load, edit or delete your saved SQL's.
- Here you can enter your own SQL query in the field or edit manually a template. When you use a Excel as input input sheet must be entered with a "$" after the name and in square brackets. You can also define a specific range for your input sheet after the "$" (e.g. sheet name: Test | use in the SQL editor: [Test$A1:G100]). If you use a folder with csv's as input you have to enter full file names with ".csv" (without a "$") in square brackets (e.g. csv file name: Test | use in the SQL editor: [Test.csv]).
- Here you can either replace placeholders defined by the selected template with your own values or define your own replacements.
- Select your output sheet from the currently open workbook from the dropdown menu.
- Optionally, you can choose whether the header should be included, the output sheet should be cleared or the output should be transposed.
- To execute the SQL query with the selected parameters, press "RUN".
- Press this button to save your currently written SQL. For more details look into the Save SQL chapter. To use this feature you must be logged in and have a valid subscription.
Data Sources and Basic Usage
SQL+ supports three types of data sources: the local workbook, other XLS workbooks, and CSV files.
Local Workbook
By default, the local workbook is the selected data source. When writing SQL, each worksheet in the local workbook can be treated as a table. The basic syntax is as follows:
SELECT * FROM [WKSNAME$]
where a “$” must be suffixed to the worksheet name and the name including the “$” must be enclosed in square brackets.
It is also possible to define a specific range within a worksheet as a table by specifying a range after the “$” sign. For example, to select the first three columns and first ten rows plus header (row one), write the following:
SELECT * FROM [WKSNAME$A1:C11]
When using the local workbook as data source, make sure the selected output sheet does not have input data because these would be overwritten by the result data.
Other XLS Workbooks
Click “Input XLS” to use another Excel workbook as data source and select the desired XLS from the file dialog that will be opened.The SQL syntax is the same as for the local workbook.
Note that generated result sets are written to the local workbook, not to the external one. Correspondingly, only local worksheets are listed in the Output Sheet dropdown.
CSV Files
Click "Input CSV" to run SQL against CSV files. This will open a CSV file dialog. Press "Select Folder" to select a folder that contains the CSV files. SQL may then be run against the CSV files within the selected folder, with each file effectively representing one table. The basic SQL syntax is as follows:
SELECT * FROM [FILEMNAME.CSV]
Note that the file extension needs to be specified and that there is no “$” suffix. Also note that it is not possible to define a table as a range within the CSV.
Saving and Re-Using SQL
Special Functions
SQL+ extends the SQL language through special functions. Currently the following three are implemented: COR, COV, and REG.
COR
This function calculates the linear correlation among selected table columns and displays the result as a correlation matrix. The usage is as follows:
SELECT COR(COL1, ..., COLn) FROM [WKSNAME$]
where COL1, ..., COLn are the names of the table columns for which correlations are to be computed.
COV
This function calculates the covariance among selected table columns and displays the result as a covariance matrix. The usage is analogous to the COR function:
SELECT COV(COL1, ..., COLn) FROM [WKSNAME$]
where COL1, ..., COLn are the names of the table columns for which covariances are to be computed.
REG
This function performs a multivariate linear regression and displays the resulting predictions and weights. The usage is as follows:
SELECT REG(X1, ..., Xn; Y) FROM [WKSNAME$]
where X1, ..., Xn are the names of the table columns used as predictors and Y is the name of the table column whose values are to be predicted.
You may include an additional parameter U in the reg function as follows:
SELECT REG(U,X1, ..., Xn; Y) FROM [WKSNAME$]
where U is the name of a column that uniquely identifies a entry in the worksheet, does providing a refernece back into the original dataset.
SQL Patterns
In the SQL Template dropdown, you may select from a list of SQL design patterns. These patterns employ placeholders (values in square brackets) for table and column names and various parameters. To adapt a pattern to your particular cause, replace its placeholders with your own values using the right pane of the SQL editor. You may also define replacements for additional parameters or clauses and apply them to a selected template or a self-defined statement.
Data Quality
- DQ.UNI: This pattern checks whether a given key (column or list of columns) is unique and, if it is not, lists all duplicates.
- DQ.REF: This pattern checks referential integrity, i.e. whether a referenced table has all the values of a key that exist in the referencing table (e.g., a PRODUCT table listing all the PRODUCT CODES for which transactions are recorded in the SALES table). If violated, all keys missing in the referenced table are listed.
- DQ.SET: This pattern compares sets of objects in two tables (each defined by a key, i.e., a column or list of columns). It returns three sets: objects that exist in the first but not in the second table, objects that exist in the second but not in the first table, objects that exist in both (the intersection).
- DQ.DEF. This pattern compares an enumerative object property across two tables (e.g., object being “employee” and property being “address”) and lists all detected differences.
- DQ.VAL. This pattern compares a numeric object property across two tables (e.g. object being “financial asset” and property being “market value”) and lists all differences above a given absolute or relative threshold.
- DQ.OUTL: This pattern compares a numeric object property across two tables and identifies statistical outliers.
Time Series
- TS.RRET: This template calculates the relative change in value from one point in time to the next.
- TS.MAVG: This template calculates a moving average over a sliding time window
Statistics
- ST.DESC: This template summarizes key statistics of a specified column, including counts, distinct values, and min/max values in descending order.
- ST.HIST: This template categorizes values into buckets, calculates the count of entries in each bucket, and computes the proportion of each bucket relative to the total count.